Avoiding the losses and waste means that our businesses are more competitive and healthy. How much do you suppose an OSHA lost time injury costs the business?
 The pain and suffering is miserable.
The pain and suffering is miserable.- There is the direct cost of the doctors, hospitals, medications, etc.
- We lose time
- having to investigate the injury and incident.,
- writing reports,
- having an OSHA investigation,
- perhaps the cost of challenging OSHA’s findings,
- legal costs for the company attorneys,
- preparing for a potential law suit,
- the cost of lost production time,
- the cost of bringing someone and train them to replace the injured person,
- the cost of lost sales,
- the cost of bad publicity,
- the cost of lower morale among the people,
- and so on.
When the safety gets right, everything else gets right as well. In this more positive culture, not only does the waste of injuries and incidents go away, people shift the way that they chose to work together resulting in other improvements like:
- fewer arguments,
- fewer grievances,
- better meetings,
- fewer meetings,
- more suggestions for improving our systems and processes,
- people taking the lead in helping to fix something that is not right,
- new ideas for better customer service emerge,
- lean manufacturing works better,
- the quality of products and services get better,
- absenteeism drops, and
- people can work together to build a better future.
Cultural improvement: bullying, harassment and dysfunction decrease.
When the safety performance and culture get better, the organization thrives.
These are things that each organization can work on right now. In Partner-Centered Leadership, Richard N. Knowles & Associates can help organizations to achieve all these things. This does not require investment.
- Get clear on your thinking and purpose.
- Go into your organization talking with and listening to the people.
- Help them to build on their ideas.
- Let them know how important they are to the success of the business.
- Do this with respect and honesty.
Change is happening all the time!
 Changes are coming fast and furious. Everything seems to be changing all around us. This can cause unsettling feelings and a loss of control. However, in the middle of all this change, one area that can be steady for us is our relationships with each other.
Changes are coming fast and furious. Everything seems to be changing all around us. This can cause unsettling feelings and a loss of control. However, in the middle of all this change, one area that can be steady for us is our relationships with each other.
If we have a good agreement about how we are going to work together including things like respect, listening, helping, learning together, these can provide us the stability we need.
These are like the pole in a subway car. With everything around us bouncing and moving, holding the pole provides the stability we need.
We can treat each other with respect,no matter what is happening in the world around us; this is within our control.
 Artificial intelligence and robots, block chains and bitcoins, the opioid epidemic, political strife, and workplace violence, international worries and potential conflicts are some of the challenges facing all of us. There is a critical need for people, in all walks of life, to come together to openly and honestly talk about our challenges, share our thinking and learn together. We do not have to be blindly swept along. We can make decisions and do the things that we need to do to help to make the world a better place.
Artificial intelligence and robots, block chains and bitcoins, the opioid epidemic, political strife, and workplace violence, international worries and potential conflicts are some of the challenges facing all of us. There is a critical need for people, in all walks of life, to come together to openly and honestly talk about our challenges, share our thinking and learn together. We do not have to be blindly swept along. We can make decisions and do the things that we need to do to help to make the world a better place. When I talk about safety. my thinking goes well beyond the traditional safety numbers, training and procedures. It includes ideas about respect and how everyone has agreed to work together. It includes ideas about personal responsibility, integrity and dedication to helping everyone improve. It includes openness, honesty and sharing information abundantly. It includes ideas about the deeper, often hidden patterns of behavior which have a profound impact on the work environment and drive much of the behavior. It includes the fact that the managers and leaders have the largest impact on their organization’s performance. It includes the understanding that managers focus on reliability, stability, predictability and control as they try to maintain the status quo and that leaders focus on the people, change and the future sharing information abundantly, treating people with respect and helping people find meaning in their work. Both good leaders and managers are needed.
When I talk about safety. my thinking goes well beyond the traditional safety numbers, training and procedures. It includes ideas about respect and how everyone has agreed to work together. It includes ideas about personal responsibility, integrity and dedication to helping everyone improve. It includes openness, honesty and sharing information abundantly. It includes ideas about the deeper, often hidden patterns of behavior which have a profound impact on the work environment and drive much of the behavior. It includes the fact that the managers and leaders have the largest impact on their organization’s performance. It includes the understanding that managers focus on reliability, stability, predictability and control as they try to maintain the status quo and that leaders focus on the people, change and the future sharing information abundantly, treating people with respect and helping people find meaning in their work. Both good leaders and managers are needed. Lots of critical knowledge, experience and skills will be lost. Younger people, who have grown up in an electronic world of texting and games, will replace these people. Many are out of shape and bordering on being over weight; some are developing diabetes. This will pose significant challenges to employers and the need to work safely and well.
Lots of critical knowledge, experience and skills will be lost. Younger people, who have grown up in an electronic world of texting and games, will replace these people. Many are out of shape and bordering on being over weight; some are developing diabetes. This will pose significant challenges to employers and the need to work safely and well.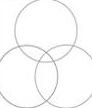 Overlap: All three of these areas of safety are often lumped together as SHE, EHS or HSE. When we lump these all together we can miss things so I think it is useful to see these three overlapping, interacting areas of our safety and health work. There is some overlap between Occupational Safety and Occupational Health like the proper selection and use of respirators. There is some area of overlap between Occupational Health and Process Safety like preventing chronic exposures to toxic chemicals. There is some overlap between Process Safety and Occupational Safety like locating trailers and offices away from operating areas using large quantities of flammable and explosive materials.
Overlap: All three of these areas of safety are often lumped together as SHE, EHS or HSE. When we lump these all together we can miss things so I think it is useful to see these three overlapping, interacting areas of our safety and health work. There is some overlap between Occupational Safety and Occupational Health like the proper selection and use of respirators. There is some area of overlap between Occupational Health and Process Safety like preventing chronic exposures to toxic chemicals. There is some overlap between Process Safety and Occupational Safety like locating trailers and offices away from operating areas using large quantities of flammable and explosive materials.




