 In my June 29th presentation at the American Society of Safety Engineers 2016 Professional Development Conference, I discussed the fact that one of the best ways for the safety professional attending the talk to help to improve the safety performance in their workplaces was to show the people that they cared about them and to enable them to make decisions about their specific work. I want to elaborate on these ideas in this newsletter. This is not just for the safety professional. This is for every team leader, supervisor, and workgroup leader. Going into your workplaces and opening up the conversations is a journey; each time you do this it gets easier and more effective. (Caring, Understanding and Openness!)
In my June 29th presentation at the American Society of Safety Engineers 2016 Professional Development Conference, I discussed the fact that one of the best ways for the safety professional attending the talk to help to improve the safety performance in their workplaces was to show the people that they cared about them and to enable them to make decisions about their specific work. I want to elaborate on these ideas in this newsletter. This is not just for the safety professional. This is for every team leader, supervisor, and workgroup leader. Going into your workplaces and opening up the conversations is a journey; each time you do this it gets easier and more effective. (Caring, Understanding and Openness!)
Meaningful caring to me means that we treat each other with respect as adults.
- As managers and supervisors we get out of our offices and go into the workplace.
- Help people to see that it is okay to talk together and be open with each other.
- We sit down together in their work place and have a cup of coffee together. We are not in a hurry just trying to make some specified number of contacts.
- We share the truth together as best we can knowing that today’s truth may be different than the truth for tomorrow because the world keeps changing, and reminding them that you’ll be back tomorrow if things have changed.
- We ask about how we each are doing. How is the day going? What good things are happening? What have we learned today or over the last few days? We listen to what we each are saying.
- We try to build on each other’s good ideas.
- We talk about how the business is doing? We talk about the contributions we are making to the success of the business.
- We discuss problems together sharing our viewpoints and seeking possible solutions. If people ask you questions which you can’t answer, tell them you do not know and will get back to them…then do it. We pay attention to the dynamics and do not over stay our visit.
As we get to know each other better we begin to explore what is really going on around here.
- Are we really doing what we say we want to be doing?
- How can our communications get clearer and better?
- What is the rumor mill saying? Talk together about the rumors and clear them up.
- Do you see better ways to go after the problems around here than we are doing? What are we missing?
- Are there hidden elephants we need to be addressing?
- When we have made a mistake, we own up to it and say we are sorry. We ask for their help.
- Are there better ways that you see to get your job done well?
- What information do you need to get your work done more effectively? Let’s talk some more about your good ideas and see if you can make some improvements.
- What is going on over and over that is really bugging you?
As you get to know the people even better, there will be opportunities to inquire about how the family is doing. You can ask…how the kids are doing in their sports and schoolwork, ask if there are things that you can be doing to help them, ask how everyone’s health is, etc. You need to use good judgment as you get into these personal conversations and not push things too far into their privacy, by accident.
These are the kinds of conversations that most of us would like to have with our own managers. How many times have you wanted to talk together with them to share an idea or problem and have not had a chance to do it? How often do you get to talk with your boss’s boss? What is important and good for you in talking with your boss is about the same as for you talking with the people in your organization about the things that are important to them.
We are all partners in making our workplaces to become healthier, physically and mentally, and helping the people in them to be the best they can be. This is a key element of Partner-Centered Safety!
 Eighty (80) pages and counting…that’s how far I got while perusing the numerous pages for the 2015 fatalities logged on OSHA reports – there were still many names and circumstances yet to read.
Eighty (80) pages and counting…that’s how far I got while perusing the numerous pages for the 2015 fatalities logged on OSHA reports – there were still many names and circumstances yet to read.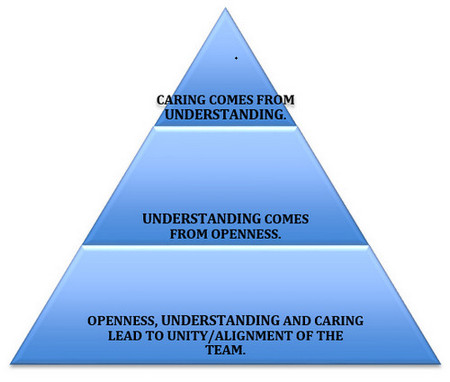



 Hardly any of us can do our best work all by ourselves.
Hardly any of us can do our best work all by ourselves. There was a video on Facebook a few weeks ago about Buddy Benches being placed in schoolyards. The video explained the importance of the communication and training that is essential to their use and effectiveness.
There was a video on Facebook a few weeks ago about Buddy Benches being placed in schoolyards. The video explained the importance of the communication and training that is essential to their use and effectiveness. In our Partner-Centered Safety realm, we go beyond this to having everyone (the people on the floor, the supervisors, the managers, and all the others) feel they are cared about. Caring means helping each other, listening to each other, sharing information, being respectful, asking for help and receiving it, looking out for each other, saying we are sorry when we make a mistake, and treating each other as whole persons. Just what caring means for people is something on which they should all agree. Management, alone, should not do it for their approach can often be quite patronizing – treating the people in the work place as if they are children. All the people, at all levels, together, need to come up with their ideas about what caring is for them. Management should not try to dictate the answers, but management needs to open up and lead this discussion about caring or it will not be addressed. Caring is visible; as is non-caring. Partner-Centered Safety is visible caring. Mistreatment of people is non-caring.
In our Partner-Centered Safety realm, we go beyond this to having everyone (the people on the floor, the supervisors, the managers, and all the others) feel they are cared about. Caring means helping each other, listening to each other, sharing information, being respectful, asking for help and receiving it, looking out for each other, saying we are sorry when we make a mistake, and treating each other as whole persons. Just what caring means for people is something on which they should all agree. Management, alone, should not do it for their approach can often be quite patronizing – treating the people in the work place as if they are children. All the people, at all levels, together, need to come up with their ideas about what caring is for them. Management should not try to dictate the answers, but management needs to open up and lead this discussion about caring or it will not be addressed. Caring is visible; as is non-caring. Partner-Centered Safety is visible caring. Mistreatment of people is non-caring. At one of the highest geographical points in Florida, at Lake Wales, is a large, 205-ft high, carillon tower. It is beautiful, as are the gardens surrounding this tower structure, made of glistening coquina stone. The tower and gardens were a gift from benefactor Edward W. Bok, who cared deeply about nature, beauty and sanctuary spaces. Millions of visitors have traversed this place of solace since it opened in 1929. Edward Bok was all about CARING for future generations – to be able to enjoy peace and beauty. His tribute signature is this:
At one of the highest geographical points in Florida, at Lake Wales, is a large, 205-ft high, carillon tower. It is beautiful, as are the gardens surrounding this tower structure, made of glistening coquina stone. The tower and gardens were a gift from benefactor Edward W. Bok, who cared deeply about nature, beauty and sanctuary spaces. Millions of visitors have traversed this place of solace since it opened in 1929. Edward Bok was all about CARING for future generations – to be able to enjoy peace and beauty. His tribute signature is this: For our workplaces, this is about the way we think about safety, the way we engage around safety, and the way we bring a third unifying force to the whole culture of safety.It’s the missing link in our respective workplaces. Without it, we tend to stay engulfed in a culture of compliance, yet despite trying and trying, we never reach excellence. Without it, we keep repeating the same mistakes – round and round we go.
For our workplaces, this is about the way we think about safety, the way we engage around safety, and the way we bring a third unifying force to the whole culture of safety.It’s the missing link in our respective workplaces. Without it, we tend to stay engulfed in a culture of compliance, yet despite trying and trying, we never reach excellence. Without it, we keep repeating the same mistakes – round and round we go. I spoke about Partner-Centered Safety™ and the importance of this as the quickest way to achieve sustainable safety excellence. As many of you know, I have written and spoken about this many times over the last several years. The information and data I share clearly shows that this approach to leading safety is very powerful, producing improved results quite quickly. Many of you have seen the terrific results the people at the DuPont, Belle Plant achieved. This approach has a very strong scientific basis in complex adaptive systems theory.
I spoke about Partner-Centered Safety™ and the importance of this as the quickest way to achieve sustainable safety excellence. As many of you know, I have written and spoken about this many times over the last several years. The information and data I share clearly shows that this approach to leading safety is very powerful, producing improved results quite quickly. Many of you have seen the terrific results the people at the DuPont, Belle Plant achieved. This approach has a very strong scientific basis in complex adaptive systems theory.
 When the Safety Culture is right…what do you see? What does Excellence look like?
When the Safety Culture is right…what do you see? What does Excellence look like?





