In this newsletter, I want to share some insights about the level of engagement of the people, the impact of low levels of engagement on profitability, safety performance, and workplace violence.
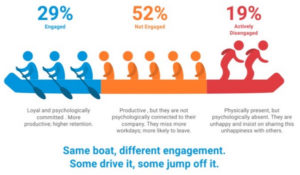
 In 2017, Gallup, Inc. published their “State of the Global Workplace,” looking at the levels of productivity around the world. They were concerned about the decline in productivity and wanted to develop a better picture of the situation. High productivity is a key to having a good quality of life, and this relates to how involved people are in their work. They found that worldwide, only about 15% of the people are highly involved. This varies from country to country with the highest levels of involvement in the USA and Canada at 31%. Those businesses in the top quartile of employee involvement in their global study are 21% more profitable and 17% more productive. They also have 70% fewer safety incidents, 40% fewer quality incidents, 41% lower absenteeism, and 59% lower turnover. The positive impact of employees being highly involved is huge.
In 2017, Gallup, Inc. published their “State of the Global Workplace,” looking at the levels of productivity around the world. They were concerned about the decline in productivity and wanted to develop a better picture of the situation. High productivity is a key to having a good quality of life, and this relates to how involved people are in their work. They found that worldwide, only about 15% of the people are highly involved. This varies from country to country with the highest levels of involvement in the USA and Canada at 31%. Those businesses in the top quartile of employee involvement in their global study are 21% more profitable and 17% more productive. They also have 70% fewer safety incidents, 40% fewer quality incidents, 41% lower absenteeism, and 59% lower turnover. The positive impact of employees being highly involved is huge.
These benefits of high levels of involvement are impressive.
In my newsletters, I have written extensively about the importance of leadership in improving involvement. Leaders focus on building respect, sharing information and making it safe for people to talk together, to share ideas and to build their future together. Leaders focus on change and improvement. Leaders also focus on helping people to see how their work is important for the success of the whole organization; this helps people to develop meaning in their work and builds commitment.
 Most people in management positions focus on systems and processes like running a payroll or production line. They want reliability, predictability, control, and stability, which are important for much of the business. But when they apply this approach to people, things go downhill. This approach results in 71% of the people globally being unengaged and 19% being actively disengaged. Morale, safety and engagement are a mess. Managers engage in managership, and this will not solve the problem of building higher levels of engagement.
Most people in management positions focus on systems and processes like running a payroll or production line. They want reliability, predictability, control, and stability, which are important for much of the business. But when they apply this approach to people, things go downhill. This approach results in 71% of the people globally being unengaged and 19% being actively disengaged. Morale, safety and engagement are a mess. Managers engage in managership, and this will not solve the problem of building higher levels of engagement.
People in manager positions need to become stronger leaders. They need to spend several hours every day with the people around them, as well as those reporting to them. They need to go into their workplaces, talking respectfully with the people, sharing information, building trust and interdependence, listening and learning together. In doing this with quality, focused conversations, people open up, share ideas and come up with better ways to do their work. When I did this when I was a Plant Manager in a chemical plant with about 1,300 people and lots of hazardous chemicals and demanding jobs, our injury rate dropped by 98%, productivity rose by 45% and earning rose by 300%. The people were involved and committed because they wanted to be. I just set the conditions where this could happen.
I need to emphasize that respect in the workplace is so very important. Lack of respect degrades everything. Lack of respect leads to harassment, bullying, sabotage, fighting, and even murder. The leaders set the tone and the standards. Bullying is a problem in over half of our workplaces and about half the bullying is from managers. This is just unacceptable. Not only does it demean the people, it causes safety problems and wrecks involvement and productivity.
If the people at the top of our organizations really want to improve involvement, the treatment of people, safety and earnings, then they can do it. It is a matter of will. The knowledge and pathways are well known and proven.
 Leaders are people who have a vision of what is possible, are concerned and care enough to make a difference, have the courage and commitment to do the work, and truly engage with people to learn, grow and to achieve their results. These are people who regularly go into their organizations, walk around, have the important conversations about getting better, building a respectful workplace, listening carefully, building trust and interdependence, and helping the people to be the best they can be. They create environments where it is safe to openly talk together, ask questions, share information, think out-loud and build a better future.
Leaders are people who have a vision of what is possible, are concerned and care enough to make a difference, have the courage and commitment to do the work, and truly engage with people to learn, grow and to achieve their results. These are people who regularly go into their organizations, walk around, have the important conversations about getting better, building a respectful workplace, listening carefully, building trust and interdependence, and helping the people to be the best they can be. They create environments where it is safe to openly talk together, ask questions, share information, think out-loud and build a better future. Lots of managers talk about the need for organizations to change and improve. But as I talk with people, go to conferences and read the safety literature, I hardly ever encounter anyone leading this way. So many managers do not know what it means to lead.
Lots of managers talk about the need for organizations to change and improve. But as I talk with people, go to conferences and read the safety literature, I hardly ever encounter anyone leading this way. So many managers do not know what it means to lead. In our Partner-Centered Safety realm, we go beyond this to having everyone (the people on the floor, the supervisors, the managers, and all the others) feel they are cared about. Caring means helping each other, listening to each other, sharing information, being respectful, asking for help and receiving it, looking out for each other, saying we are sorry when we make a mistake, and treating each other as whole persons. Just what caring means for people is something on which they should all agree. Management, alone, should not do it for their approach can often be quite patronizing – treating the people in the work place as if they are children. All the people, at all levels, together, need to come up with their ideas about what caring is for them. Management should not try to dictate the answers, but management needs to open up and lead this discussion about caring or it will not be addressed. Caring is visible; as is non-caring. Partner-Centered Safety is visible caring. Mistreatment of people is non-caring.
In our Partner-Centered Safety realm, we go beyond this to having everyone (the people on the floor, the supervisors, the managers, and all the others) feel they are cared about. Caring means helping each other, listening to each other, sharing information, being respectful, asking for help and receiving it, looking out for each other, saying we are sorry when we make a mistake, and treating each other as whole persons. Just what caring means for people is something on which they should all agree. Management, alone, should not do it for their approach can often be quite patronizing – treating the people in the work place as if they are children. All the people, at all levels, together, need to come up with their ideas about what caring is for them. Management should not try to dictate the answers, but management needs to open up and lead this discussion about caring or it will not be addressed. Caring is visible; as is non-caring. Partner-Centered Safety is visible caring. Mistreatment of people is non-caring. There are three main aspects to Partner-Centered Safety.
There are three main aspects to Partner-Centered Safety. But, the machine view of organizations is the dominant paradigm right now. We direct the people to work in tight procedures. We manipulate them to do things right. We punish them when there is an injury or incidents. We look for root-cause. We think that if we can take things apart and understand the parts that we can understand the whole. Almost all the effort is engaged in doing things TO the people as if they were just interchangeable parts of a machine. Most people push back against authority in this paradigm. This is a win/lose environment.
But, the machine view of organizations is the dominant paradigm right now. We direct the people to work in tight procedures. We manipulate them to do things right. We punish them when there is an injury or incidents. We look for root-cause. We think that if we can take things apart and understand the parts that we can understand the whole. Almost all the effort is engaged in doing things TO the people as if they were just interchangeable parts of a machine. Most people push back against authority in this paradigm. This is a win/lose environment. People are often reluctant to speak up in these negative environments. Ideas for improvement never surface. New employees are negatively influenced and led astray. Supervisors have a very rough time getting the people to do their work properly. Grievance rates are high and much time is wasted needlessly because these are not addressed at an early stage.
People are often reluctant to speak up in these negative environments. Ideas for improvement never surface. New employees are negatively influenced and led astray. Supervisors have a very rough time getting the people to do their work properly. Grievance rates are high and much time is wasted needlessly because these are not addressed at an early stage. As managers go into their workplaces, walking around watching, listening and sharing with true authenticity and interest, trust and interdependence build. People learn to open up, to share, to point out possible areas for improvement, and to realize that they are a critical part of the whole safety effort. A huge, positive shift in the safety culture occurs. The people close to the actual, physical work are often in the best position to see potential hazards that are not visible to the managers. The managers often need to push to meet production schedules so it is easy for them to miss these potential hazards. Therefore, having the active help of those closest to the work is an important piece of the total safety effort. This is one way we avoid disasters like the Deepwater Horizon explosion and fire.
As managers go into their workplaces, walking around watching, listening and sharing with true authenticity and interest, trust and interdependence build. People learn to open up, to share, to point out possible areas for improvement, and to realize that they are a critical part of the whole safety effort. A huge, positive shift in the safety culture occurs. The people close to the actual, physical work are often in the best position to see potential hazards that are not visible to the managers. The managers often need to push to meet production schedules so it is easy for them to miss these potential hazards. Therefore, having the active help of those closest to the work is an important piece of the total safety effort. This is one way we avoid disasters like the Deepwater Horizon explosion and fire. Things do not have to be this way! Most of the people know that this is counter-productive but that is the way it is. However, when we engage the people from across the organization in the Complexity Leadership Process, guiding them in a purposeful conversation of discovery that changes everything, they find it does not have to be that way!
Things do not have to be this way! Most of the people know that this is counter-productive but that is the way it is. However, when we engage the people from across the organization in the Complexity Leadership Process, guiding them in a purposeful conversation of discovery that changes everything, they find it does not have to be that way!