In my last Safety newsletter, I wrote about the need to significantly improve our safety performance.
 I feel we are not moving fast enough to get to higher levels of performance. Way too many people are getting hurt and killed. Safety is a part of all we are doing and the whole system needs to be making improvements.
I feel we are not moving fast enough to get to higher levels of performance. Way too many people are getting hurt and killed. Safety is a part of all we are doing and the whole system needs to be making improvements.
A big step was taken towards this goal in a Safety II in Practice Workshop in Saint Petersburg, Florida, on February 24-27, 2019. This excellent gathering was organized and brought together by Tom McDaniel, a widely experienced, practical safety leader. One speaker was Eric Hollnagel who has written several books about Safety II. He summarizes Safety II as “the ability to succeed under varying conditions, so that the number of intended and acceptable outcomes is as high as possible. The Safety II perspective looks at how work goes well and tries to understand how that happens in order to ensure that it will happen again.” The shift from Safety I, where we look at what went wrong, to Safety II where we look at what is going right and learn from it is critical for our work to attain higher levels of performance.
Tom McDaniel spoke of our obligation to present the closest interpretation of the truth in our organizations enabling the people to be given enough information to make the best possible decisions. We need to engage the people to help to improve our total performance including safety and reducing the number of incidents and injuries. We need to understand and build upon the things that people are doing right. He shared many practical examples to illustrate this.
Ron Gantt spoke about the need to widen our gaze to see the complex interactions of everyday work so we can see opportunities for improvement and facilitation rather only violations. He talked about the importance of going into our organizations, being with the people and seeing how they really do their work and the challenges they face every day as they get the jobs done. It is important to close the gap between work-as-imagined and work-as-done.
Our Safety I habits are strong and it is not easy to move into a Safety II approach and sustain it. Safety I and Safety II are not in opposition to each other. Rather we need to take the best of the basic rules, procedures and skills of Safety I, and build the positive approach of Safety II into our way of working with the people at all levels in the organization so that everyone can be the best they can be.
 I was given the opportunity to talk about my work on Partner-Centered Leadership and shared information about the Process Enneagram, which is such a powerful tool to help people to come together to solve their complex problems. Partner-Centered Leadership is focused on sharing information, building trust and interdependence, helping everyone see the importance of their work for the success of the whole enterprise and moving into a better future. Everyone at the workshop was seeking ways to actually move into Safety II and make it happen so there was a lot of interest in this work.
I was given the opportunity to talk about my work on Partner-Centered Leadership and shared information about the Process Enneagram, which is such a powerful tool to help people to come together to solve their complex problems. Partner-Centered Leadership is focused on sharing information, building trust and interdependence, helping everyone see the importance of their work for the success of the whole enterprise and moving into a better future. Everyone at the workshop was seeking ways to actually move into Safety II and make it happen so there was a lot of interest in this work.
Tom McDaniel was gracious in commenting:
“Dick Knowles has the most effective process for understanding and measuring leadership and its advancement. His knowledge on this subject is outstanding. He brings clarity to what many are already doing in an ad hoc method but by seeing this relationship distinction, it can only help you and your organization move further along. I know he has written a couple of books on this. He has helped many organizations succeed.”
This Workshop was an exciting step into a brighter future for the people in our organizations. Many thanks to Tom McDaniel for having organized this workshop and bringing everyone together to share and learn.
 A review of the Bureau of Labor Statics summary of fatal occupational injuries for 2011-2017 shows a 1% drop in fatalities from 2016 to 2017 to a total of 5,147 people having lost their lives at work. This is about 9% higher than the 4,693 people killed in 2011. The top three 2017 fatalities categories are roadway accidents totaling 1,299 (up 15% since 2011); slips, trips and falls totaling 887 (up 23% since 2011); and murders and suicides totaling 733 (up by only 2% since 2011).
A review of the Bureau of Labor Statics summary of fatal occupational injuries for 2011-2017 shows a 1% drop in fatalities from 2016 to 2017 to a total of 5,147 people having lost their lives at work. This is about 9% higher than the 4,693 people killed in 2011. The top three 2017 fatalities categories are roadway accidents totaling 1,299 (up 15% since 2011); slips, trips and falls totaling 887 (up 23% since 2011); and murders and suicides totaling 733 (up by only 2% since 2011). We need courageous leaders who focus on the people, change and the future. Leaders value sharing information, building trust and interdependence, and helping people to see how their job is important for the success of the whole venture.
We need courageous leaders who focus on the people, change and the future. Leaders value sharing information, building trust and interdependence, and helping people to see how their job is important for the success of the whole venture. Go into your organizations listening to and talking with the people. Share your vision. Build trust and interdependence. Create safe spaces for people to talk with each other, to share and create the future. Everything will change. That is what I experienced at the Belle Plant.
Go into your organizations listening to and talking with the people. Share your vision. Build trust and interdependence. Create safe spaces for people to talk with each other, to share and create the future. Everything will change. That is what I experienced at the Belle Plant. As I travel around and watch things happening, I see so many people in a big hurry. We are coming to the end of the good weather so people are hurrying to get outside jobs finished up. Roofers are really busy and not taking the time to properly use and secure their fall protection. I read of a recent 29-story fall in New York City when a guy on a big construction site fell through an unsecured hole in the floor.
As I travel around and watch things happening, I see so many people in a big hurry. We are coming to the end of the good weather so people are hurrying to get outside jobs finished up. Roofers are really busy and not taking the time to properly use and secure their fall protection. I read of a recent 29-story fall in New York City when a guy on a big construction site fell through an unsecured hole in the floor. A good, proven approach is to have brief start up meetings to review the hazards of the day’s work, making sure we have the right PPE and other equipment in place and used, asking each other about what might go wrong and working to avoid this. We need to look over the schedules and be sure we have the equipment we need and the right people for the work.
A good, proven approach is to have brief start up meetings to review the hazards of the day’s work, making sure we have the right PPE and other equipment in place and used, asking each other about what might go wrong and working to avoid this. We need to look over the schedules and be sure we have the equipment we need and the right people for the work. The American Society for Safety Engineers (soon to be The American Society for Safety Professionals) in Denver, Colorado, on June 19-22, 2017, was attended by about 5,000 people. This was a record for attendance. There were lots of papers and a huge trade show exhibit. I never saw so much safety equipment and other offerings.
The American Society for Safety Engineers (soon to be The American Society for Safety Professionals) in Denver, Colorado, on June 19-22, 2017, was attended by about 5,000 people. This was a record for attendance. There were lots of papers and a huge trade show exhibit. I never saw so much safety equipment and other offerings.

 Each time the construction cycle picks up, more people get killed, mostly from falls. Some falls are the result of poor footing. Some falls result from poor housekeeping and clutter. Some falls result from inadequate barricading of edges or open holes in the floors. Some falls result from poor pre-shift preparations and the work is started before things are ready. Some falls result from people rushing to get the work done quickly. Some falls result from some people being careless.
Each time the construction cycle picks up, more people get killed, mostly from falls. Some falls are the result of poor footing. Some falls result from poor housekeeping and clutter. Some falls result from inadequate barricading of edges or open holes in the floors. Some falls result from poor pre-shift preparations and the work is started before things are ready. Some falls result from people rushing to get the work done quickly. Some falls result from some people being careless. With all the uncertainties and variable working conditions, all of you need to be looking out for each other – I mean really watching and helping each other. Being ready and willing to stop unsafe work is important. It is critical that information flows freely so that everyone knows what is going on and are able to work closely together.
With all the uncertainties and variable working conditions, all of you need to be looking out for each other – I mean really watching and helping each other. Being ready and willing to stop unsafe work is important. It is critical that information flows freely so that everyone knows what is going on and are able to work closely together. In many of our newsletters, I have talked about helping organizations co-create their safety future using the
In many of our newsletters, I have talked about helping organizations co-create their safety future using the  Eighty (80) pages and counting…that’s how far I got while perusing the numerous pages for the 2015 fatalities logged on OSHA reports – there were still many names and circumstances yet to read.
Eighty (80) pages and counting…that’s how far I got while perusing the numerous pages for the 2015 fatalities logged on OSHA reports – there were still many names and circumstances yet to read.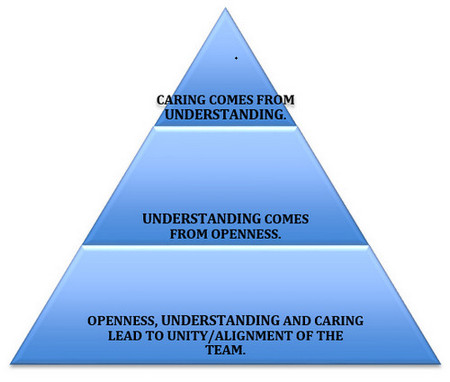



 There was a video on Facebook a few weeks ago about Buddy Benches being placed in schoolyards. The video explained the importance of the communication and training that is essential to their use and effectiveness.
There was a video on Facebook a few weeks ago about Buddy Benches being placed in schoolyards. The video explained the importance of the communication and training that is essential to their use and effectiveness.




